Female Hair Thinning Explained: Root Causes, Medical Treatments & Prevention
How to Stop Female Hair Thinning: Causes and Treatments (2026 Guide)

Female hair thinning is one of the most common—yet misunderstood—hair concerns among women. Unlike sudden hair loss or patchy conditions, thinning happens gradually, often going unnoticed until volume significantly decreases. The good news? In many cases, hair thinning in women is preventable and reversible when addressed early.
This guide explains the real causes of female hair thinning, how to stop it effectively, and which treatments actually work—without repeating common hair care advice you’ve already seen everywhere.
What Is Female Hair Thinning?
Female hair thinning is a gradual decrease in hair density and volume, not the sudden loss of large amounts of hair. Instead of falling out in clumps, individual strands become finer, weaker, and shorter over time, making the scalp more visible—especially at the crown, top of the head, or along the part line.
Unlike male pattern baldness, female hair thinning usually does not cause a receding hairline. Most women retain their frontal hairline while noticing reduced fullness and overall thickness.
How Female Hair Thinning Develops
When the hair growth cycle is disturbed, hair thinning happens.. Each strand spends less time in the growth phase and more time in the resting phase. Over time, new hair grows back:
- Thinner in diameter
- Shorter in length
- Slower than before
As this cycle repeats, overall hair density decreases.
Hair Thinning vs. Hair Loss: Key Differences
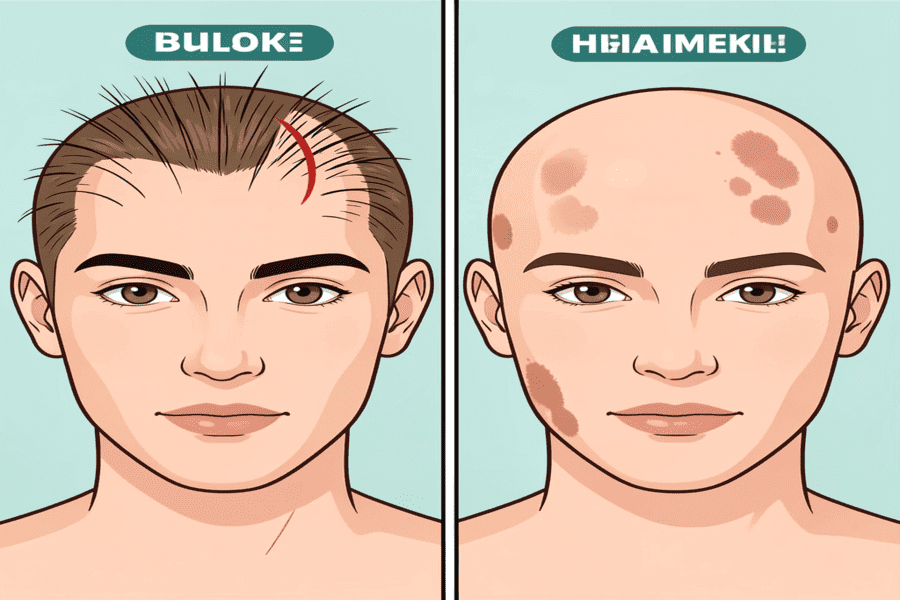
Although often confused, hair thinning and hair loss are not the same condition.
Hair Thinning
- Hair strands gradually become finer
- Overall volume decreases
- Scalp visibility increases over time
- Hairline usually stays intact
- Shedding may appear normal
Hair Loss
- Excessive daily shedding
- Noticeable clumps of hair
- Bald patches or receding areas
- Sudden or rapid onset
Most women experience diffuse thinning, meaning hair becomes sparse across the scalp rather than disappearing in specific spots.
Why Women Commonly Experience Thinning Instead of Baldness
Women’s hair follicles are typically more resistant to complete shutdown. Instead of stopping growth entirely, follicles miniaturize, producing thinner strands rather than no hair at all. This is why female hair thinning often progresses slowly and can go unnoticed for months or even years.
Is Female Hair Thinning a Normal Part of Aging?
Some degree of thinning can occur with age due to hormonal changes and slower cell turnover. However, noticeable or early hair thinning is not something women should ignore, as it often signals underlying factors such as hormonal imbalance, nutritional deficiency, stress, or scalp health issues.
Early identification makes hair thinning much easier to manage and treat.
Early Signs of Hair Thinning in Women

Recognizing the early signs of hair thinning is essential, as timely action can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Hair thinning usually develops slowly and silently, making it easy to overlook until noticeable volume loss occurs.
Common Early Warning Signs
Women experiencing early-stage hair thinning may notice one or more of the following changes:
- Wider part line: The scalp becomes more visible along the natural part, especially under overhead lighting
- Thinner ponytail or braid: Hair ties may wrap around more times than before
- Scalp visibility in bright light: Hair appears fine or sparse when exposed to sunlight or indoor lighting
- Slower hair regrowth: Hair takes longer to grow after trimming or shedding
- Loss of volume without excessive shedding: Hair looks flat or limp despite normal daily hair fall
Subtle Changes Many Women Miss
Not all signs are obvious. Early thinning can also present as:
- Reduced fullness around the crown
- Difficulty holding styles that once lasted all day
- Hair that feels lighter or less dense when touched
Because shedding often remains within a normal range, many women assume nothing is wrong.
Why These Signs Appear Early
Hair thinning occurs when follicles begin producing progressively finer strands. This process starts long before visible hair loss, which is why these signs may appear months before noticeable thinning or scalp exposure.
Why Early Detection Matters
The earlier hair thinning is identified:
- The more follicles can be preserved
- The better the response to treatment
- The greater the chance of regaining density
Ignoring early symptoms may allow thinning to progress to more advanced stages.
Main Causes of Female Hair Thinning
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones play a critical role in regulating hair growth. Even minor shifts in hormone levels can disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing thinner, weaker strands over time. Hormonal imbalances are among the most common causes of female hair thinning, especially in women over 30.
Key Hormonal Triggers
- Estrogen Decline (Perimenopause & Menopause):
Estrogen helps maintain the hair in its growth phase. During perimenopause and menopause, declining estrogen levels shorten this growth phase, resulting in gradual thinning, particularly at the crown and part line. - Post-Pregnancy Hormonal Changes:
After childbirth, estrogen and progesterone levels drop rapidly. Many women notice postpartum shedding, often most noticeable 2–4 months after delivery. This type of thinning is usually temporary but can be distressing. - Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
Women with PCOS often have higher androgen levels, which can miniaturize hair follicles and lead to thinning, especially along the central scalp. - Thyroid Disorders (Hypo- or Hyperthyroidism):
Thyroid hormones regulate hair follicle metabolism. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause diffuse hair thinning and changes in hair texture.
How Hormonal Imbalance Affects Hair Growth
Low estrogen or increased androgen sensitivity shortens the anagen (growth) phase of hair follicles. Over time, this leads to:
- Finer, weaker strands
- Reduced overall density
- Increased scalp visibility
- Slower regrowth after shedding
Addressing hormonal imbalances early, through medical evaluation and treatment, can often slow or reverse thinning.
2. Nutritional Deficiencies
Hair follicles are highly sensitive to nutrient shortages. The most common deficiencies linked to thinning include:
- Iron (even without anemia)
- Vitamin D
- Protein insufficiency
- Zinc deficiency
Crash dieting or restrictive eating plans often worsen hair thinning.
3. Chronic Stress & Cortisol
Stress is more than a mental challenge—it directly affects hair growth at the follicle level. Prolonged emotional or physical stress increases cortisol, the body’s stress hormone, which can push hair follicles into the telogen (resting) phase prematurely.
How Stress Affects Hair
Elevated cortisol disrupts the hair cycle, leading to:
- Reduced regrowth: Hair takes longer to replace lost strands
- Thinner hair strands: Follicles produce weaker, finer hair
- Delayed recovery: It can take months for normal hair growth to resume
Why Stress-Related Thinning Can Be Reversible
Unlike genetic thinning, stress-induced hair loss is often temporary. By managing stress through:
- Adequate sleep
- Mindfulness or meditation
- Balanced lifestyle and regular exercise
…hair follicles can return to a normal growth cycle, restoring thickness and volume over time.
4. Scalp Health & Circulation Issues
Healthy hair starts with a healthy scalp.Hair follicles require proper blood flow, oxygen, and nutrients to function. Disruptions in scalp health can weaken follicles and trigger thinning.
Common Scalp-Related Causes of Thinning
- Constant tension hairstyles: Tight ponytails, braids, or buns cause traction on follicles
- Infrequent scalp cleansing: Oil, sweat, and product buildup can clog follicles
- Inflammatory scalp conditions: Dermatitis, psoriasis, or fungal infections can reduce follicle activity
How Poor Circulation Impacts Hair Growth
Reduced blood flow and inflammation limit nutrient delivery to hair follicles, shortening the growth phase and resulting in finer, less dense hair.
Simple improvements, such as gentle scalp massages and proper hygiene, can enhance follicle function and prevent further thinning.
5. Genetic Female Pattern Thinning
Also known as female pattern hair thinning, this type of hair loss is hereditary and usually affects the crown and part line. It tends to develop gradually over time.
Key Features
- Thinning is diffuse, not patchy
- The hairline generally remains intact
- Progression is gradual but often noticeable in the 30s or 40s
Managing Genetic Thinning
While you cannot change your genetics, early intervention can slow progression and improve hair density. Treatments may include:
- Topical therapies like minoxidil
- Professional treatments like PRP (platelet-rich plasma)
- Lifestyle support such as nutrition and stress management
Recognizing genetic thinning early allows women to preserve as much hair density as possible.
Medical & Clinical Treatments for Female Hair Thinning
When lifestyle adjustments and nutritional improvements aren’t enough, medical and clinical treatments can help restore hair density and slow thinning. These treatments are most effective when started early in the thinning process.
Minoxidil Therapy
Minoxidil is currently the most clinically supported treatment for female hair thinning. It is a topical solution or foam that acts directly on hair follicles.
How Minoxidil Works:
- Extends the hair growth phase (anagen): Keeps hair in its active growth stage longer
- Improves follicle size: Leads to thicker, stronger strands
- Enhances scalp blood flow: Increases oxygen and nutrient delivery to follicles
Timeline for Results:
Visible improvement typically occurs within 3–6 months, with continued use necessary to maintain results. Early intervention yields the best outcomes.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy uses your own blood plasma, enriched with growth factors, injected into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles.
Benefits of PRP for Hair Thinning:
- Activates dormant follicles
- Promotes improved hair density
- Slows the progression of thinning
Best Candidates:
PRP is most effective for women with early-stage thinning, where follicles are still active but producing finer strands.
Hormonal Evaluation & Treatment
If hair thinning is linked to hormonal imbalances, correcting the root cause is essential. A doctor may recommend:
- Thyroid treatment: To normalize hypo- or hyperthyroidism
- Hormone regulation: Addressing estrogen, progesterone, or androgen imbalances
- Nutritional correction: Supplementing deficiencies in iron, vitamin D, or protein
Hormone-related thinning often responds well to treatment, especially when combined with lifestyle adjustments.
Microneedling (Clinical)
Microneedling performed by a professional creates tiny micro-injuries in the scalp, which stimulates collagen production and increases blood flow.
How it helps hair thinning:
- Enhances nutrient delivery to follicles
- Supports absorption of topical treatments like minoxidil
- May reactivate follicles in early-stage thinning
Note: Clinical microneedling is recommended over at-home devices for safety and effectiveness.
Key Takeaway
Medical treatments for female hair thinning are most effective when started early. Combining clinical interventions with nutritional support, scalp care, and stress management provides the best chance of slowing thinning and promoting fuller hair.
.
Natural Ways to Stop Hair Thinning in Women

While medical treatments are effective, many women can support hair follicle health naturally through lifestyle, diet, and scalp care. These approaches work without relying on commercial products and are safe to implement at home.
1. Scalp Stimulation
A healthy scalp encourages stronger, thicker hair growth. Gentle stimulation improves blood flow, delivering nutrients and oxygen to hair follicles.
Tips for Scalp Stimulation:
- Daily gentle massage: Use fingertips in small circular motions for 5–10 minutes
- Increase circulation: Light tapping or brushing can stimulate follicles
- Reduce tension buildup: Loosen tight hairstyles and avoid prolonged pulling on hair
Regular scalp stimulation can help hair follicles remain active and maintain growth.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Nutrition directly affects hair density. A diet that reduces inflammation and provides essential nutrients supports healthy hair growth.
Key Foods to Include:
- Lean protein: Chicken, fish, eggs, and legumes for keratin production
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts to nourish follicles
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and broccoli for iron, vitamin A, and antioxidants
- Iron-rich foods: Red meat, beans, and fortified cereals to prevent deficiency
Pro Tip: Avoid crash diets or excessive calorie restriction, which can trigger thinning.
3. Stress Regulation
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which can push hair follicles into the resting phase, leading to thinning. Reducing stress supports normal hair growth.
Effective Stress Management Techniques:
- Prioritize adequate sleep (7–9 hours per night)
- Practice mindfulness, meditation, or breathing exercises daily
- Avoid chronic overexertion in work or exercise routines
Even small changes in stress management can have a noticeable effect on hair health.
4. Gentle Hair Practices
Handling hair carefully reduces mechanical stress on follicles and prevents further thinning.
Gentle Hair Care Tips:
- Steer clear of tight hairstyles that tug on follicles, such as buns or ponytails.
- Reduce friction during washing by using smooth motions and wide-tooth combs
- Treat wet hair carefully: Avoid aggressive towel drying because wet hair is more delicate.
These habits help maintain hair density and prevent breakage over time.
Key Takeaway
Combining scalp stimulation, a nutrient-rich diet, stress management, and gentle hair practices can significantly slow hair thinning and support overall follicle health. These natural strategies complement medical treatments and can be implemented safely at home.
Is Female Hair Thinning Reversible?
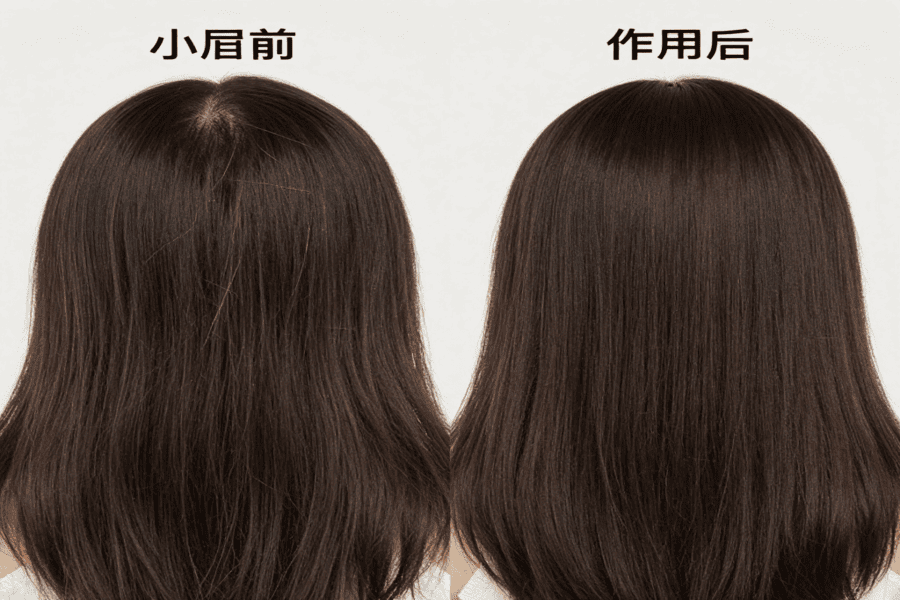

Female hair thinning can often be reversed, but the extent of recovery depends on the underlying cause. Identifying the trigger early is crucial for restoring hair density effectively.
Reversible Causes
Hair thinning caused by nutritional deficiencies is usually reversible. Correcting low levels of iron, vitamin D, protein, or zinc allows hair follicles to resume normal growth, gradually restoring thickness.
Stress-related thinning is also highly reversible. Once chronic stress is managed—through adequate sleep, mindfulness, and balanced lifestyle habits—hair follicles can return to a healthy growth cycle.
Post-partum thinning typically resolves naturally within six to twelve months after childbirth, as hormonal levels stabilize, allowing hair to regrow without medical intervention.
Partially Reversible Causes
Some causes require more targeted intervention and may only be partially reversible. Hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid disorders or perimenopause, can improve with medical treatment or hormone regulation, but results vary depending on severity and age.
Genetic female pattern thinning cannot be fully reversed because it is inherited. However, early intervention using treatments like minoxidil, PRP therapy, and supportive lifestyle measures can slow progression and help maintain existing hair density.
Importance of Early Action
Early detection and treatment are key. Addressing hair thinning promptly helps preserve follicles, improve response to treatments, and prevent permanent density loss. Waiting too long can result in miniaturized follicles and reduced hair thickness, which are more difficult to restore.
Key Takeaway
Most forms of hair thinning—especially those caused by nutrition, stress, or post-pregnancy changes—are highly reversible with proper care. Hormonal and genetic causes require long-term management, but early action still provides the best chance for maintaining healthy, dense hair.
Prevention Tips for Long-Term Hair Density
Maintaining healthy hair requires a combination of nutrition, scalp care, and lifestyle habits. These steps help prevent further thinning and support long-term hair density.
Regular Health Checks
Annual blood tests for iron, vitamin D, and other key nutrients can help detect deficiencies before they affect hair growth. Correcting deficiencies early ensures follicles receive the nutrients they need to stay active and strong.
Smart Diet and Lifestyle Choices
Avoid extreme dieting or highly restrictive eating plans, as these can deprive hair follicles of essential nutrients and trigger thinning. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and vitamins supports healthy hair growth over time.
Protecting the Hair and Scalp
Rotating hairstyles and avoiding tight ponytails, braids, or buns reduces traction on follicles, preventing tension-related thinning. Additionally, addressing scalp irritation, inflammation, or buildup early can preserve follicle health and prevent long-term damage.
Seek Early Medical Advice
Consulting a healthcare professional at the first signs of noticeable thinning ensures timely diagnosis and management. Early intervention can slow progression and improve the effectiveness of treatments.
When to See a Dermatologist
Even with preventive measures, some signs indicate it’s time to see a specialist. You should seek professional advice if you notice:
- Rapid or sudden thinning, especially over a few weeks or months
- Scalp itching, redness, or irritation
- Family history of female pattern thinning, which may increase risk
- No improvement after 6 months of lifestyle and nutritional adjustments
A dermatologist can perform diagnostic tests, recommend medical treatments, and monitor progress, ensuring thinning is addressed appropriately before it becomes more severe.
Final Thoughts
Female hair thinning is more than a cosmetic concern—it can be an early signal that your body is experiencing hormonal, nutritional, or stress-related imbalances. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for effectively stopping thinning and restoring healthier, fuller hair.
The Importance of Early Intervention
The sooner hair thinning is identified, the greater the chance of preserving hair density and preventing further loss. Combining medical treatments, natural care strategies, and lifestyle adjustments provides the best outcomes.
A Positive Outlook
With timely intervention, consistent care, and proper treatment, many women can successfully slow or even reverse hair thinning. By focusing on overall health and follicle support, it’s possible to maintain strong, vibrant hair well into 2026 and beyond.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can female hair thinning grow back naturally?
Yes. Hair thinning caused by stress, nutritional deficiencies, or hormonal changes is often reversible when addressed early. Timely intervention and proper care can restore hair density over time.
What vitamin deficiencies cause hair thinning in women?
The most common contributors are iron, vitamin D, protein, and zinc deficiencies. Correcting these deficiencies through diet or supplementation can improve hair growth and strength.
Does female hair thinning mean baldness?
No. Most women experience diffuse thinning, where hair becomes finer and less dense across the scalp, rather than complete bald patches.
How long does it take to see results from hair thinning treatments?
Visible improvement from treatments such as minoxidil, PRP therapy, or lifestyle interventions usually appears within 3–6 months. Consistency is key for optimal results.
Is female pattern hair thinning permanent?
Female pattern thinning is manageable but not fully curable. Early detection and treatment help preserve existing hair density and slow progression, even though genetics cannot be changed.
Disclaimer
This article should not be used in place of professional medical advice; it is intended just as information. For the diagnosis or treatment of disorders affecting the hair or scalp, always seek the advice of a trained healthcare professional.