Hair Shedding vs Hair Loss: What’s Normal? (USA 2026)
Is Daily Hair Fall Normal or a Sign of Hair Loss?
Experiencing daily hair loss is typical; however, distinguishing between what is normal and what might signal an issue can be perplexing Seeing hair in the shower drain, on your pillow, or in your brush often causes panic, even though hair shedding vs hair loss has different implications. Some hair shedding is a natural part of the hair growth cycle, while actual hair loss may signal an underlying issue.
In this guide, we break down normal hair shedding vs hair loss in a clear, practical way. You’ll learn how much hair fall is normal, the early signs that may indicate true hair loss, and the most common causes behind both conditions. We’ll also cover effective solutions—from simple lifestyle and diet changes to medical treatments recommended by U.S. dermatologists.
Explore this resource to see how topics like ‘Shower Hair Loss: Causes & Remedies’ and ‘Alopecia Areata & Causes of Female Hair Loss’ relate, giving a better perspective on hair shedding to hair loss For medically accurate advice, all information aligns with the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), a trusted authority on hair and scalp health.
Table of Contents
What Is Hair Shedding?
What Is Hair Loss?
Normal Hair Shedding vs Hair Loss — Key Differences
Common Causes of Hair Shedding
How to Tell If Your Hair Fall Is Normal or Not
When to See a Doctor
Treatment Options for Hair Shedding
Effective Hair Care Tips to Limit Hair Loss
FAQs
Conclusion
What Is Hair Shedding?
Hair shedding vs hair loss is a topic that often confuses many people. Hair shedding is a completely normal part of your hair growth cycle, but understanding it can help you distinguish natural shedding from actual hair loss. Knowing the difference is key to maintaining healthy hair and avoiding unnecessary worry. Here’s a closer look at what hair shedding entails.
The Natural Hair Growth Cycle
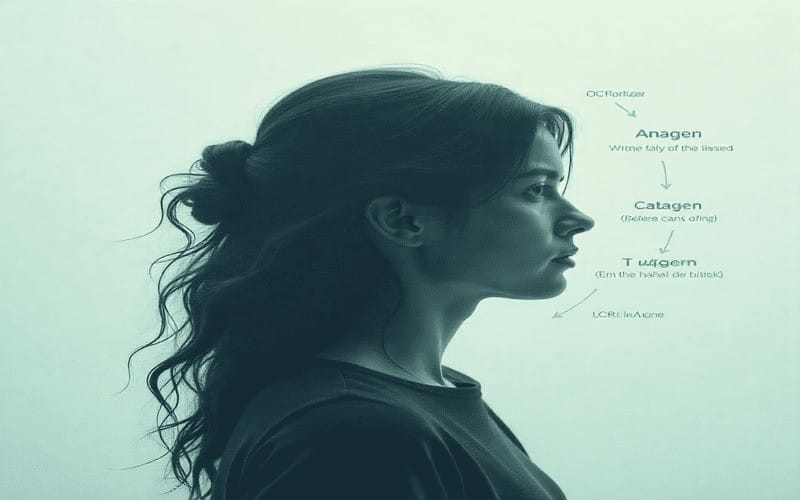

Every hair on your scalp goes through three phases:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): The hair grows actively for 2–7 years.
- Catagen (Transition Phase): Growth slows, and the follicle shrinks for about 2–3 weeks.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): Old hairs fall out to make way for new ones, lasting 2–4 months.
The telogen phase is when most normal shedding occurs, signaling that your hair is healthy and regenerating. Understanding this phase helps you differentiate hair shedding vs hair loss.
How Many Hairs Fall Daily?
- 50 to 100 hairs are usually lost each day.
- Slight variations are common due to stress, diet, hormonal changes, or seasonal differences.
Losing more than this consistently may indicate hair loss, rather than natural shedding. For more guidance, see our guide, ‘Shower Hair Loss: Causes & Remedies.

Seasonal Hair Shedding
- Some people notice more hair fall in fall and spring, which is called seasonal shedding.
- This happens because the body naturally adjusts to environmental changes, daylight hours, and temperature.
Seasonal shedding is temporary and usually resolves on its own, but tracking it helps distinguish normal hair shedding vs hair loss.
How Hair Shedding Differs From Hair Loss
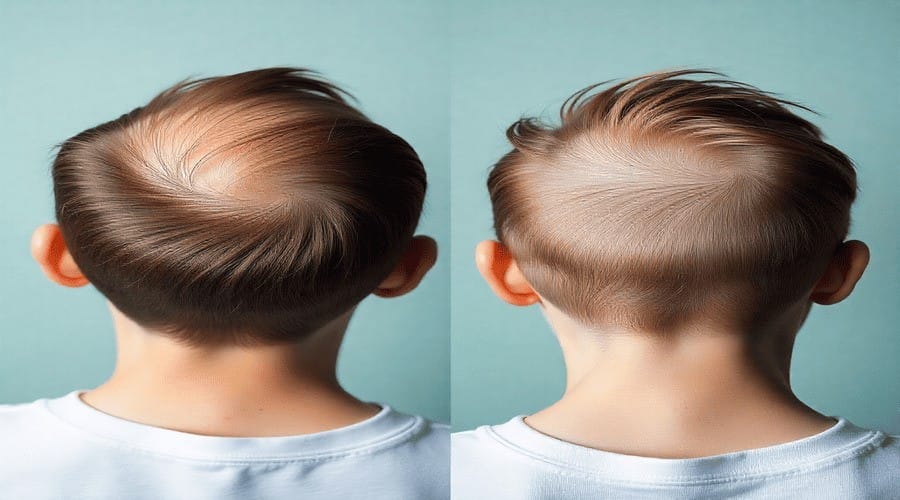
- Hair shedding: Even, predictable, part of the natural growth cycle.
- Hair loss: Irregular, patchy, or excessive, often accompanied by thinning or bald spots.
To gain a clearer understanding of the distinction between hair shedding and hair loss, check out our guide, ‘Shower Hair Loss: Causes & Remedies,’ and consider the advice from the American Academy of Dermatology
What Is Hair Loss?
Hair shedding vs hair loss is a distinction many people overlook. Hair loss is more than just noticing strands on your pillow or in the shower—it’s a sign that the hair growth cycle is being disrupted. Unlike normal shedding, hair loss often indicates an underlying issue that may require attention. Understanding its causes and types can help you take the right steps early and protect long-term hair health.
Hair Loss Explained in Simple Terms
Hair loss occurs when hair follicles are damaged or inactive, preventing new hair from growing. While hair shedding is part of a healthy cycle, hair loss is irregular and excessive, often leading to thinning or bald patches if not addressed.
Think of shedding as a routine “hair refresh,” while hair loss is a warning that your scalp or overall health needs care. Recognizing the difference between hair shedding vs hair loss is the first step toward timely intervention.
The Role of Hair Follicle Damage
Hair follicles are tiny pockets in your scalp that produce hair. Damage to these follicles—due to genetics, illness, hormonal changes, or trauma—can prevent hair from regrowing properly:
- Damaged follicles = weaker, thinner hair
- Chronic damage = permanent hair loss
For insights into hair follicle health, see our guide, ‘Alopecia Areata & Female Hair Loss Causes
Temporary vs Permanent Hair Loss
- Temporary Hair Loss: Often triggered by stress, illness, medications, or postpartum changes. After the trigger is eliminated, hair typically grows back.
- Permanent Hair Loss: Caused by genetic factors like androgenetic alopecia, scarring, or long-term follicle damage.
Early detection is crucial—temporary hair loss can become permanent if not managed promptly. Understanding hair shedding vs hair loss helps you take early action.
Why Hair Loss Is More Serious Than Shedding
- Hair loss may indicate medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune issues, or nutritional deficiencies.
- It can lead to visible thinning or bald spots, affecting confidence and scalp health.
- Unlike normal shedding, it often requires medical treatment or lifestyle changes.
For evidence-based recommendations, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) provides guidelines on diagnosis and treatment: AAD Hair Loss.
Normal Hair Shedding vs Hair Loss — Key Differences
Many people wonder whether the hair they’re losing is part of normal shedding or actual hair loss. Understanding the key differences can help you take timely action and protect your scalp and hair health. This section breaks down the differences clearly using the most important factors, helping you distinguish hair shedding vs hair loss effectively.
Amount of Hair Fall
- Normal Hair Shedding: Losing 50–100 hairs per day is considered normal and part of the natural hair growth cycle.
- Hair Loss: Losing more than 100 hairs daily, or noticing hair falling in clumps, may indicate a problem.
Duration (Short-term vs Long-term)
- Normal Shedding: Usually short-term or seasonal (fall & spring), resolving on its own within a few weeks.
- Hair Loss: Long-term, often persistent for months or years if the underlying cause isn’t addressed.
Temporary shedding can become chronic if triggers like stress, illness, or hormonal imbalances persist. Learn more about hair loss patterns at the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD).
Hair Regrowth Presence
- Normal Shedding: Hair naturally regrows from follicles without noticeable thinning.
- Hair Loss: Hair may not regrow in certain areas, especially in cases of follicle damage or genetic conditions.
For tips on promoting hair regrowth, check our detailed guide: HairBreaking: Why It Happens and How to Fix It.
Scalp Visibility
- Normal Shedding: Scalp looks healthy with no visible thinning.
- Hair Loss: Thinning or bald patches may appear, particularly along the hairline or crown.
Early signs are subtle—look for widening parts or extra scalp visibility in natural light. Check out ‘Alopecia Areata & Female Hair Loss Causes’ for advice on identifying hair loss
Hair Thickness Changes
- Normal Shedding: Hair maintains its usual thickness and strength.
- Hair Loss: New hair may grow thinner or weaker, and over time overall hair density decreases.
Maintaining a balanced diet and proper hair care routine is crucial for hair thickness. Learn more about healthy hair care here: Hair Care Tips for HealthyHair.
Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | Normal Hair Shedding | Hair Loss |
| Amount of Hair Fall | 50–100 hairs/day | >100 hairs/day, clumps |
| Duration | Short-term, seasonal | Long-term, persistent |
| Hair Regrowth | Full regrowth | May not regrow |
| Scalp Visibility | No noticeable thinning | Thinning or bald patches |
| Hair Thickness | Normal | Thinner, weaker strands |
Summary
Understanding the difference between normal hair shedding vs hair loss is the first step in protecting your hair health. While shedding is natural, hair loss can indicate underlying issues that require attention. Early recognition allows you to adopt gentle hair care practices, make lifestyle adjustments, and seek professional guidance when necessary. For evidence-based recommendations, refer to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and explore our related articles on hair care and hair loss causes.
Common Causes of Hair Shedding
Hair shedding is a natural process, but certain factors can temporarily increase the amount of hair you lose. Understanding these triggers helps distinguish normal hair shedding vs hair loss and allows you to take steps to minimize excessive fall. Recognizing the cause also ensures you can act early if shedding becomes more serious.
Stress and Illness
High stress levels or serious illnesses can trigger a condition called telogen effluvium, where hair enters the resting phase prematurely, leading to temporary shedding.
Managing stress through exercise, meditation, or professional support can help restore hair growth. For a detailed guide on stress-related hair loss, see AAD – Hair Loss Guide.
Post-Pregnancy Hair Shedding
After pregnancy, many women notice increased hair fall due to hormonal shifts, particularly the drop in estrogen levels:
- Shedding usually starts 2–4 months postpartum.
- In most cases, hair will naturally regrow within 6–12 months.
Learn more about post-pregnancy hair changes in our guide: Alopecia Areata & Female Hair Loss Causes.
Weight Loss
Rapid or extreme weight loss can affect nutrient intake, leading to temporary shedding. Deficiencies in iron, protein, and vitamins may weaken hair follicles.
A balanced diet rich in protein and iron supports healthy hair growth. Check our guide: Hair Care Tips for Healthy Hair.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations—such as thyroid disorders, menopause, or changes in birth control—can disrupt the hair growth cycle and trigger shedding:
- Women are especially affected during perimenopause and menopause.
- Proper medical evaluation can help identify the root cause.
For more on hormones and hair health, visit: American Thyroid Association –Hair Loss and Hormones.
Medications
Certain medications may lead to temporary hair shedding as a side effect. Common culprits include:
Blood thinners – can affect circulation and hair growth
Chemotherapy drugs – often cause temporary hair loss
Beta-blockers – may contribute to thinning in some individuals
Retinoids – Medications or topical treatments derived from vitamin A that, in some cases, may contribute to hair thinning or shedding.
Seasonal Changes
Some people experience slightly increased hair shedding in the fall and spring, a natural adjustment by the body to environmental changes:
- Seasonal hair loss is generally short-lived.
- Hair density usually returns to normal after a few weeks.
Monitoring seasonal patterns helps detect real hair loss early. Also read: Shower Hair Loss: Causes & Remedies.
How to Tell If Your Hair Fall Is Normal or Not

Distinguishing normal hair shedding vs hair loss can be tricky, but simple at-home checks can help you understand whether your hair fall is within a healthy range or a sign of a problem. These practical methods are recommended by dermatologists in the USA and are easy to perform without special tools.
The Pull Test
The pull test helps determine if your hair is shedding excessively.
How to do it:
- Take a small section of hair (about 20–30 strands) between your fingers.
- Gently tug and see how many hairs come out.
Interpretation:
- Losing 1–2 hairs is normal.
- Losing more than 5 hairs per pull consistently may indicate hair loss.
Learn more about evaluating hair fall: Shower Hair Loss: Causes & Remedies.
External reference: American Academy of Dermatology – Hair Loss.
The Ponytail Test
The ponytail test is a quick visual check for hair density.
How to do it:
- Gather your hair into a ponytail using a soft hair tie.
- Observe the thickness of the ponytail.
Interpretation:
- A full, consistent ponytail usually indicates normal shedding.
- Noticeable thinning or a very small ponytail may signal hair loss.
For tips on maintaining hair density, see: Hair Care Tips for Healthy Hair.
Shower Drain Observation
Many people first notice hair shedding in the shower drain.
What to do:
- Pay attention to how much hair collects after washing.
- Track patterns over a week.
Interpretation:
- Occasional hair strands are normal.
- Consistent clumps may indicate abnormal hair loss.
Check related guidance: Alopecia Areata & Female Hair Loss Causes.
Timeline Check (3-Month Rule)
Hair shedding caused by stress, illness, or other temporary factors usually resolves within 3 months.
How to use the timeline:
- Monitor your hair over a 3-month period.
- If excessive shedding continues beyond this timeframe, it may indicate chronic hair loss requiring professional evaluation.
For understanding long-term hair loss patterns, visit: American Academy of Dermatology – Hair Loss Guide.
Summary
By using simple at-home tests like the pull test, ponytail test, shower drain observation, and following the 3-month rule, you can assess whether your hair fall is normal hair shedding vs hair loss. Early detection allows you to take action—through lifestyle adjustments or professional treatment—to maintain strong, healthy hair.
When to See a Doctor

Recognizing the signs of serious hair loss early can help prevent permanent thinning. While normal hair shedding is part of the natural cycle, certain symptoms indicate the need for professional evaluation. Knowing these warning signs ensures timely action and helps maintain long-term hair health.
Hair Falling in Clumps
If you notice large amounts of hair coming out in clumps, it may indicate telogen effluvium or another medical condition.
Bald Patches
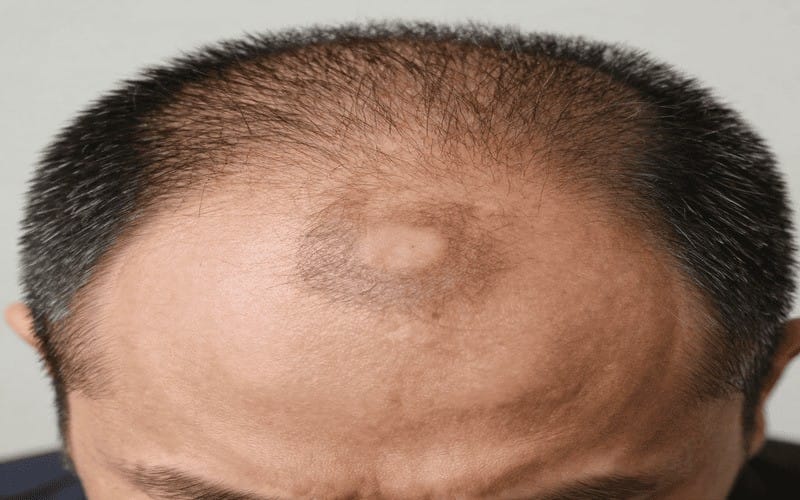
Sudden bald spots on your scalp, eyebrows, or other areas may indicate alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition. Early treatment increases the chances of regrowth.
Related guide: Alopecia Areata & Female Hair Loss Causes.
Sudden Thinning
Gradual or sudden thinning across the scalp may indicate androgenetic alopecia or nutritional deficiencies. Regular monitoring is important to catch issues early and differentiate normal hair shedding vs hair loss.
Itching, Pain, or Redness
Scalp discomfort, inflammation, or redness may suggest infections, scalp conditions, or dermatitis, which can lead to hair loss if untreated.
External reference: Mayo Clinic – Hair Loss Causes.
Hair Loss Lasting Over 6 Months
Hair shedding or thinning that continues beyond six months is considered chronic and warrants professional evaluation. Early consultation with a dermatologist or trichologist ensures proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options for Hair Shedding
If your hair fall is primarily normal hair shedding, lifestyle and self-care adjustments can help maintain healthy hair and reduce shedding naturally.
Stress Management
- Reduce stress through meditation, yoga, or regular exercise.
- Stress is a major trigger for temporary hair shedding (telogen effluvium).
Related tips: Balance Hormones Supplements: How to Naturally RestoreHormonal Health.
Diet Improvements
- Eat a balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to promote healthy hair growth.
- Stay hydrated to nourish the scalp and support overall hair health.
Iron, Protein & Vitamin Intake
- Key nutrients such as iron, zinc, vitamin D, and biotin are essential for strong hair follicles.
- Deficiencies in these nutrients may contribute to increased hair shedding.
External reference: Harvard Health – Nutrients for Hair Growth.
Gentle Hair Care Routine
- Minimize damage by avoiding tight hairstyles, harsh chemicals, and frequent heat styling.
- Choose gentle products like mild shampoos and conditioners that match your hair type.
Internal link: Hair Care Tips for Healthy Hair
Natural Remedies
- Scalp massage with oils, aloe vera, or mild herbal treatments can improve circulation.
- These remedies support natural hair growth and reduce shedding.
Understanding the difference between hair shedding vs hair loss ensures that these remedies are applied effectively and appropriately.
Treatment Options for Hair Shedding
If your hair fall is primarily normal hair shedding, lifestyle and self-care adjustments can help maintain healthy hair and reduce shedding naturally.
Stress Management
- Reduce stress through meditation, yoga, or regular exercise.
- Stress is a major trigger for temporary hair shedding (telogen effluvium).
Related tips: Balance Hormones Supplements: How to Naturally RestoreHormonal Health.
Diet Improvements
- Eat a balanced diet including plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to promote healthy hair growth.
- Stay well-hydrated to keep your scalp nourished and support overall hair health.
Iron, Protein & Vitamin Intake
- Essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, vitamin D, and biotin help maintain strong hair follicles.
- Lack of these nutrients can contribute to increased hair shedding.
External reference: Harvard Health – Nutrients for Hair Growth.
Gentle Hair Care Routine
- Limit damage by avoiding tight hairdos, strong chemicals, and excessive use of heat tools.
- Use hair-friendly products such as gentle shampoos and conditioners matched to your hair type.
Related guide: Hair Care Tips for Healthy Hair.
Natural Remedies
- Scalp massage with oils, aloe vera, or mild herbal treatments can improve circulation.
- These remedies support natural hair growth and reduce shedding.
Understanding the difference between hair shedding vs hair loss ensures that these remedies are applied effectively and appropriately.
Effective Hair Care Tips to Limit Hair Loss

Maintaining healthy hair isn’t just about treatments—it’s also about daily habits and care routines. Following these simple tips can help reduce hair shedding, strengthen follicles, and prevent long-term hair loss. Understanding the difference between normal hair shedding vs hair loss ensures these habits are applied effectively.
Avoid Tight Hairstyles
- Hairstyles like ponytails, braids, buns, or extensions can put excessive tension on hair follicles, leading to traction alopecia over time.
- Opt for loose hairstyles and soft hair ties to protect your scalp.
Related guide: Hair Breaking: Why It Happens and How to Fix It.
Reduce Heat Styling
- Excessive use of hair dryers, straighteners, or curling irons weakens hair strands.
- When styling, avoid using too much heat and always wear a heat protectant.
Related guide: Hair Gloss Treatments for Healthy Hair.
Scalp Massage
- Regular scalp massages increase blood flow to hair follicles, promoting growth and strengthening strands.
- You can use light oils like coconut or argan oil for added nourishment.
Related guide: American Academy of Dermatology – Hair Care.
Use Mild Shampoos
- Using strong shampoos may strip your hair of its natural oils, leading to dryness and fragility
- Choose sulfate-free or gentle shampoos suitable for your hair type.
Related guide: Olaplex Hair Mask Guide – No 8, 4-in-1, and Dupes.
Proper Nutrition
- Hair health depends heavily on diet and nutrient intake.
- Include foods rich in protein, iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamins A, C, and D.
- Stay hydrated, as water supports hair growth and scalp health.
Related guide: Balance Hormones Supplements: How to Naturally RestoreHormonal Health.
Summary
Simple daily hair care practices—combined with a balanced diet and gentle styling habits—can significantly reduce hair shedding and support healthy hair growth. Incorporate these tips consistently to maintain strong, thick, and resilient hair, and always monitor changes to distinguish normal hair shedding vs hair loss for early intervention if needed.
FAQs
Q1. Is hair shedding normal every day?
Yes, daily hair shedding is normal.Daily hair loss of 50–100 strands is typical and reflects the natural hair growth process. Hair enters the telogen (resting) phase, falls out, and is replaced by new growth.
For further details concerning typical hair shedding and hair cycles, kindly consult: Shower Hair Loss: Causes & Remedies.
Q2. How much hair fall is normal in the shower?
It’s common to notice a few strands of hair in the shower. Losing a handful of hairs per wash is normal. However, large clumps or consistent excessive shedding may signal underlying hair loss rather than normal shedding.
Q3. Can stress cause hair shedding?
Yes. Stress is a major trigger for temporary hair shedding, also called telogen effluvium. Elevated stress levels can cause a greater number of hair follicles to enter the resting phase, resulting in heightened hair shedding.
Tips for managing stress-related hair fall: Balance Hormones Supplements:How to Naturally Restore Hormonal Health.
External reference: American Academy of Dermatology – Stress and Hair Loss.
Q4. Does hair shedding grow back?
In most cases, yes. Hair that falls out due to normal shedding or temporary factors (stress, postpartum changes, diet) typically regrows within a few months. Persistent thinning may require evaluation by a dermatologist.
Discover additional information: Causes of Alopecia Areata and Female Hair Loss.
Q5. Is hair loss reversible?
It depends on the cause:
- Temporary hair loss (stress, illness, nutritional deficiencies) is usually reversible once the underlying cause is addressed.
- Genetic or permanent hair loss (androgenetic alopecia, follicle scarring) may require medical treatments like Minoxidil, PRP therapy, or lifestyle changes to manage and stimulate regrowth.
Expert guidance: American Academy of Dermatology – Hair Loss Treatments.
Conclusion
- Maintaining healthy hair requires an understanding of the distinction between hair loss and shedding.
While losing 50–100 hairs daily is normal, persistent or excessive hair loss may signal underlying issues requiring attention. Early detection allows you to take preventive measures through gentle hair care routines, proper nutrition, and stress management. If hair loss continues or worsens, consulting a dermatologist or hair specialist ensures effective treatment and helps prevent permanent thinning. For more guidance, explore our related articles on shower hair loss and alopecia causes.





